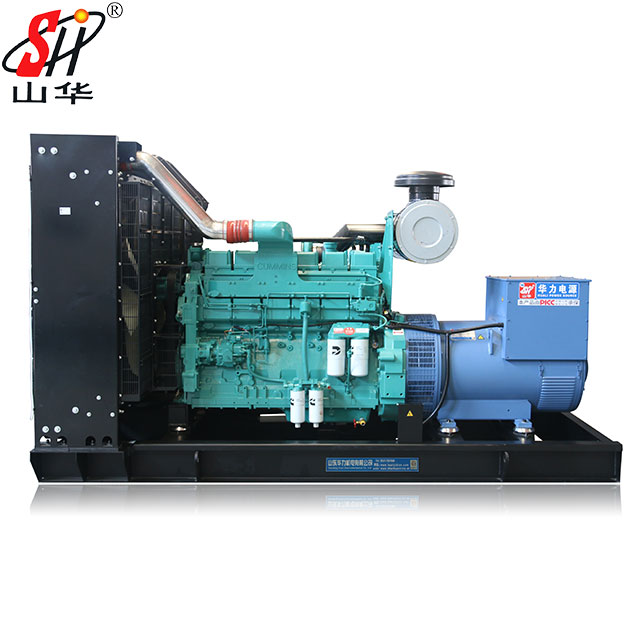
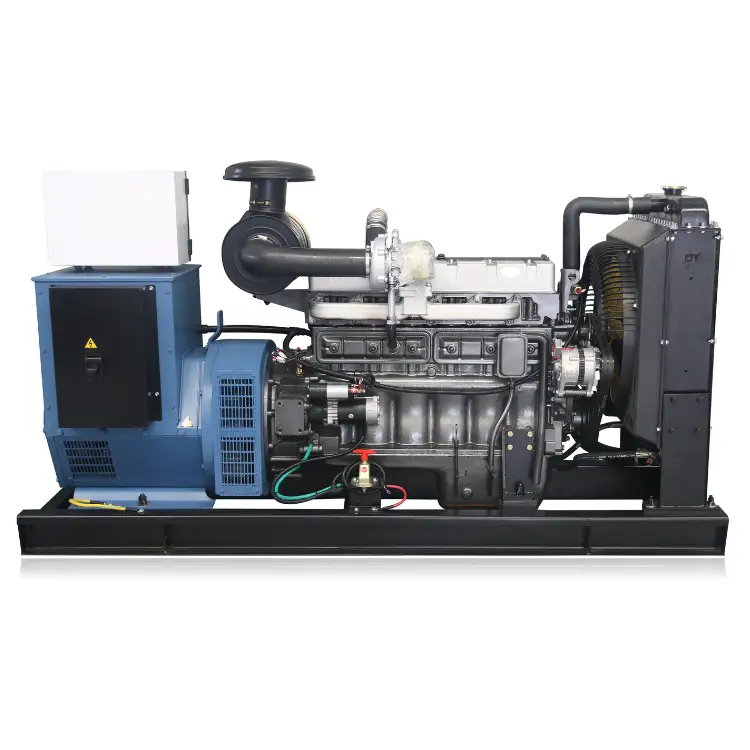
In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, hydrogen generator Cummins diesel systems represent a pivotal innovation. Hydrogen, a clean and potent fuel source, stands at the forefront of alternative energy technologies, promising a significant reduction in carbon emissions. The elemental appeal of hydrogen lies in its abundance and high energy yield when combined with oxygen, producing only water as a byproduct. This characteristic positions hydrogen as a quintessential sustainable fuel for future energy demands.
Cummins Inc., traditionally known for its robust diesel engines, has increasingly pivoted towards embracing and enhancing hydrogen technologies. The history of Cummins’s involvement in diesel technology stretches over a century, during which it has established a reputation for reliability and efficiency. However, recognizing the environmental impacts of diesel fuels, Cummins has committed to advancing hydrogen technology, which aligns with global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. This transition is marked by significant R&D investments aimed at developing hydrogen-powered engines and generators that offer comparable power and efficiency to traditional diesel systems without the environmental toll.
Cummins’s journey into hydrogen technology not only exemplifies the company’s adaptability but also its dedication to pioneering clean energy solutions. As stated by Cummins CEO Tom Linebarger, “Our investment in hydrogen-powered technologies is geared towards creating a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future, ensuring our products continue to deliver exceptional performance while significantly reducing our ecological footprint.” This strategic shift underscores Cummins’s role in shaping a greener, more sustainable future in power generation.
The introduction of hydrogen fuel technology by companies like Cummins and others signifies a transformative period in the energy sector, promising advancements that could fundamentally alter how industries operate and how communities are powered. With hydrogen at its core, the future of sustainable power looks not only viable but vibrant.
The Basics of Hydrogen Generators: How They Work
Hydrogen generators are at the cutting edge of fuel technology, enabling the efficient production of hydrogen gas, which is then used to power engines and turbines similar to those found in hydrogen generator Cummins diesel systems. The primary operation of these generators involves the process of electrolysis, which is the separation of water (H₂O) into its basic components – hydrogen and oxygen – using an electric current.
The core components of a hydrogen generator include:
- Electrolyzer Cell: This is where the electrolysis of water occurs. An electrical current passes through the water, causing the hydrogen and oxygen atoms to separate.
- Power Supply: Provides the necessary electrical energy to drive the electrolysis process.
- Gas Purification System: After production, the hydrogen gas often contains impurities that must be removed. This system purifies the hydrogen to ensure it is suitable for use in engines or fuel cells.
- Storage and Pressure Control Units: These components handle the storage and delivery of hydrogen at the correct pressure levels required for various applications.
The operation of a hydrogen generator is based on the principle that when electrical energy is introduced into water containing an electrolyte (to improve conductivity), hydrogen gas forms at the cathode (the negative pole) and oxygen forms at the anode (the positive pole). This method is not only effective but also scalable, allowing for both small and large-scale production of hydrogen.
One of the key advantages of using hydrogen generators is their ability to produce hydrogen on-demand, which reduces the need for extensive storage infrastructures and minimizes the risks associated with transporting hydrogen. Additionally, when powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, hydrogen generators can produce hydrogen with virtually no carbon emissions, making them integral to Cummins diesel strategies for sustainable energy solutions.
As highlighted by Dr. Samuel Wright, a leading researcher in hydrogen fuel technology, “Hydrogen generators are transformative tools in our move towards decarbonization. Their integration into industries traditionally dominated by fossil fuels represents a critical step towards achieving global sustainability goals.”
Understanding these fundamental workings and components is crucial as industries increasingly adopt hydrogen technology, marking a significant shift from conventional fuel systems to more sustainable alternatives.
Cummins’s Role in Hydrogen Generator Development
Cummins Inc. has strategically positioned itself as a leader in the transition from traditional diesel engines to advanced hydrogen generator Cummins diesel technologies. This transition is part of a broader initiative to embrace cleaner energy solutions in response to global environmental challenges. Cummins’s approach to hydrogen technology involves both innovation in new products and adaptations of existing ones to accommodate hydrogen fuel.
Cummins’s transition from diesel to hydrogen: Cummins has long been synonymous with durable and efficient diesel engines. However, the company has recognized the imperative to reduce carbon emissions and has thus committed significant resources to developing hydrogen-based technologies. Their efforts include modifying traditional diesel engines to run on hydrogen and developing new hydrogen fuel cell solutions.
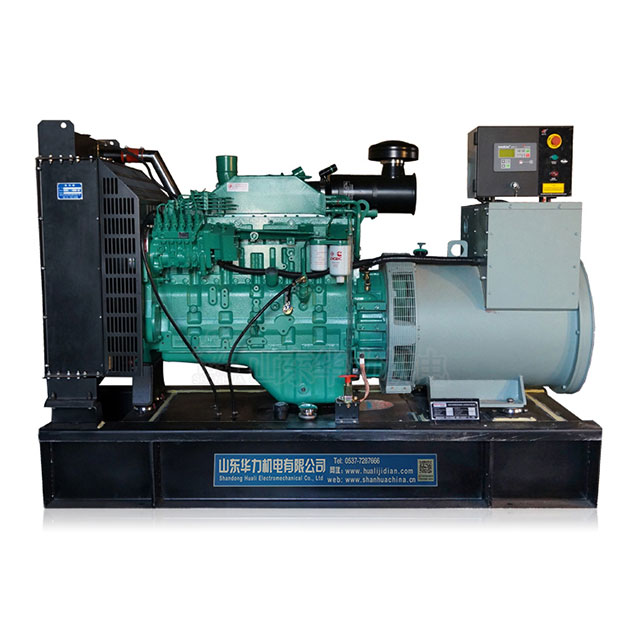
Recent projects and partnerships: Cummins has been actively involved in several high-profile projects aimed at demonstrating the viability and efficiency of hydrogen fuel technologies. One notable project is their collaboration with Shandong Huali Electromechanical Co., Ltd. to develop and deploy hydrogen-fueled power solutions for industrial applications. This partnership reflects Cummins’s strategy of collaborating with regional leaders to facilitate the adoption of hydrogen technologies globally.
Moreover, Cummins has launched initiatives to power commercial vehicles with hydrogen fuel cells, showcasing the practical application of this technology in transportation. These projects not only demonstrate the company’s commitment to innovation but also help in setting industry standards for hydrogen use in commercial settings.
Cummins’s role in developing hydrogen generators is reinforced by its participation in international forums and consortia dedicated to hydrogen energy. Their leadership in these forums highlights the company’s influence in shaping the future of hydrogen technology. For instance, Tom Linebarger, CEO of Cummins, emphasized the importance of such initiatives, stating, “By leading the way in hydrogen technology, we are not only contributing to decarbonizing the environment but also creating sustainable solutions that meet our customers’ needs without compromising on performance.”
The efforts of Cummins in hydrogen generator development signify a monumental shift in the energy sector, promoting a sustainable future while continuing to deliver high-performance power solutions. Their work in this field not only enhances their product offerings but also aligns with global sustainability goals, positioning Cummins as a pivotal player in the energy transition landscape.
Comparative Analysis: Hydrogen Generators vs. Diesel Generators
The transition towards sustainable energy solutions has sparked a significant debate between the use of hydrogen generator Cummins diesel systems and traditional diesel generators. This comparative analysis delves into the efficiency, environmental impact, and overall sustainability of these two types of generators.
Efficiency Comparisons: Hydrogen generators boast a higher efficiency in energy conversion compared to traditional diesel generators. Hydrogen fuel cells, for example, convert chemical energy directly into electrical energy with efficiencies potentially exceeding 60%, compared to diesel engines, which generally operate at around 40% efficiency. This higher efficiency can result in significant energy savings over time.
Environmental Impact Analysis: The environmental benefits of hydrogen generators are substantial. Hydrogen generators produce zero emissions at the point of use—water is the only byproduct, making them a cornerstone for green energy initiatives. In contrast, diesel generators emit carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, which contribute to air pollution and global warming. Cummins diesel generators modified to use hydrogen can drastically reduce these harmful emissions, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
Sustainability and Long-Term Viability: Hydrogen has the potential for renewable production via electrolysis using wind, solar, or hydroelectric power. This creates a cycle that can be nearly emission-free from production to power generation, enhancing the sustainability of hydrogen as a fuel source. Diesel, however, is a fossil fuel with a finite supply and involves environmentally damaging extraction and refining processes.
The discussion of hydrogen versus diesel is not merely academic but is rooted in practical implications for the future of energy. As noted by environmental expert Dr. Hannah Green, “Adopting hydrogen generators is not only about reducing emissions but also about building resilient and sustainable energy systems that can withstand future environmental and market shifts.”
In conclusion, while diesel generators have been the backbone of industrial power for decades, the advantages of hydrogen—especially in terms of efficiency and environmental impact—present a compelling case for its increased adoption. The transition led by companies like Cummins reflects a broader industry move towards sustainable practices, which is essential for meeting future energy demands without compromising the health of the planet.
Challenges and Opportunities in Hydrogen Generator Implementation
The implementation of hydrogen generator Cummins diesel technologies, while promising, presents a set of unique challenges and opportunities that shape the landscape of sustainable power generation.
Technical Challenges: The adoption of hydrogen generators involves overcoming several technical barriers. One of the primary concerns is the storage and transportation of hydrogen. Hydrogen has a low volumetric energy density and requires high pressures, advanced materials, and innovative technologies for safe and efficient storage. Additionally, retrofitting existing infrastructure to accommodate hydrogen, particularly in industries traditionally reliant on diesel, poses significant engineering and financial challenges.
Economic Implications: The initial costs associated with hydrogen generator systems are notably higher than those for conventional diesel generators. These costs include the installation of hydrogen production facilities, refueling stations, and the generators themselves. However, the long-term savings in fuel costs and maintenance, coupled with potential government incentives for clean energy technologies, can offset these initial investments.
Market Opportunities: Despite these challenges, the shift toward hydrogen power also presents substantial market opportunities. As industries and governments increasingly focus on reducing carbon emissions, the demand for clean energy solutions like hydrogen generators is expected to grow. This market trend is supported by the development of more cost-effective electrolysis technologies and the global expansion of renewable energy sources, which can provide the electricity needed for hydrogen production.
Regulatory Environment: The regulatory environment is also evolving to support hydrogen energy solutions. Governments worldwide are implementing policies that promote the use of clean energy, which includes subsidies for hydrogen technology projects, tax incentives, and grants for research and development. These initiatives are crucial for overcoming economic hurdles and encouraging the adoption of hydrogen technologies.
The integration of hydrogen generators into mainstream energy systems requires careful consideration of these challenges and opportunities. According to energy policy expert Dr. Lisa Ford, “The road to hydrogen adoption is complex and requires coordinated efforts between governments, industries, and researchers to address these challenges effectively. Yet, the environmental and economic benefits make it a journey worth pursuing.”
Overall, while the path to widespread implementation of hydrogen generators is fraught with challenges, the enduring benefits—ranging from environmental sustainability to energy security—offer compelling reasons to advance this clean technology. This dynamic field promises not only to innovate but also to revolutionize how we think about and use energy in the future.
Future Prospects: Innovations in Hydrogen Generator Technology
As the hydrogen generator Cummins diesel market evolves, continuous innovations and research are paving the way for more efficient and practical hydrogen energy solutions. These developments are critical for the future integration of hydrogen technology into various sectors including transportation, industrial power, and residential energy.
Emerging Technologies in Hydrogen Generation and Storage: Innovations in hydrogen generation are primarily focused on enhancing the efficiency and reducing the costs of electrolysis—the process by which electrical energy is used to produce hydrogen from water. Advanced materials and novel electrolyte solutions are being explored to increase the conductivity and stability of electrolyzer cells, thus improving overall energy efficiency. In terms of storage, researchers are developing solid-state hydrogen storage methods, which could offer safer and more compact alternatives to high-pressure gas or cryogenic liquid storage.
Cummins’s Research and Development Efforts: Cummins is at the forefront of these technological advancements. Their research teams are working on next-generation fuel cell technologies and hydrogen internal combustion engines that offer cleaner combustion and higher efficiency. These developments are not isolated but are part of broader industry collaborations intended to standardize and scale hydrogen technologies.
Cummins’s commitment to R&D in hydrogen technology is exemplified by their strategic investments in startups and academic institutions that are leading in clean energy research. By fostering innovation through partnerships, Cummins ensures it stays at the cutting edge of technology while also promoting a more widespread adoption of hydrogen solutions.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources: Another significant area of innovation involves integrating hydrogen production with renewable energy sources. This integration is vital for producing “green hydrogen” (hydrogen produced through renewable means) at a scale and cost that are competitive with traditional energy sources. Cummins is exploring opportunities to use excess renewable energy—a common occurrence during peak production periods—to power electrolysis, thereby turning a potential inefficiency in the renewable sector into a productive asset for hydrogen generation.
These innovations highlight the dynamic nature of the hydrogen energy sector and underscore the potential for hydrogen to become a cornerstone of global energy strategies. As noted by renewable energy specialist Dr. Emily Tran, “The synergy between renewable energy and hydrogen production creates a sustainable loop that could drastically cut our reliance on fossil fuels and make clean energy accessible worldwide.”
The advancements in hydrogen generator technology not only promise to enhance environmental sustainability but also to revolutionize energy systems globally. Cummins’s ongoing efforts in this field are indicative of their role not just as a participant but as a leader in the energy transition, driving both technological and societal shifts towards a more sustainable future.
Conclusion: Envisioning the Role of Hydrogen in Future Energy Systems
The exploration of hydrogen generator Cummins diesel technologies illuminates a path towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future in power generation. Cummins’s role in this transformative journey underscores the potential of hydrogen to replace or complement traditional fossil fuels across various sectors, from industrial applications to transportation and emergency power systems.
The integration of hydrogen as a key energy source is driven not only by its environmental benefits—such as reduced emissions and reliance on renewable resources—but also by significant advancements in technology that enhance the efficiency and feasibility of hydrogen generators. The case studies we’ve examined demonstrate the practicality and benefits of hydrogen power, showcasing substantial reductions in carbon emissions, improved energy efficiency, and robust performance in critical applications.
However, the transition to hydrogen power is not without challenges. The economic, technical, and regulatory hurdles that currently hinder widespread adoption require coordinated efforts among governments, industries, and the scientific community. Continued investment in research and development, coupled with supportive policies and incentives, is crucial for overcoming these barriers and fostering a conducive environment for hydrogen energy.
As we move forward, the focus should be on scaling up technologies and creating infrastructures that facilitate the seamless integration of hydrogen into our energy systems. The commitment of companies like Cummins to advancing hydrogen technology is a testament to the viable role hydrogen can play in achieving global energy sustainability and decarbonization goals.
In conclusion, the shift towards hydrogen energy, led by innovations in hydrogen generator technologies and strategic partnerships, presents a promising avenue for building a cleaner, more sustainable future. The ongoing advancements and real-world applications of hydrogen power not only reflect the potential of this energy source but also highlight the imperative for continued progress and adaptation in our global energy strategies.
FAQs: Common Questions About Hydrogen Generator Cummins Diesel
Q1: What is a hydrogen generator Cummins diesel? A hydrogen generator Cummins diesel refers to a system developed by Cummins that combines hydrogen fuel technology with traditional diesel engine frameworks. These systems utilize hydrogen as the primary fuel to generate power, offering a cleaner alternative to solely diesel-powered units by significantly reducing emissions of harmful pollutants.
Q2: How does a hydrogen generator improve sustainability? Hydrogen generators enhance sustainability by using hydrogen, a clean fuel that, when consumed, emits only water vapor and no carbon dioxide. This drastically reduces greenhouse gas emissions and helps in combating air pollution and global warming. Additionally, when hydrogen is produced from renewable energy sources, the entire energy supply chain can become nearly carbon-neutral.
Q3: Are hydrogen generators commercially available? Yes, hydrogen generators, including those developed by companies like Cummins, are increasingly becoming commercially available. These systems are being implemented in various sectors including industrial manufacturing, public transportation, and emergency backup systems. Their availability is expected to rise as technology advances and production costs decrease.
Q4: What are the main challenges facing the adoption of hydrogen generators? The primary challenges include high initial costs, the need for extensive infrastructure for hydrogen production and refueling, and technical issues related to storage and transportation of hydrogen. Overcoming these barriers requires technological advancements, governmental support through subsidies and incentives, and increased public and private investments.
Q5: How does Cummins contribute to the advancement of hydrogen technology? Cummins is actively involved in research and development of hydrogen technologies. They have formed partnerships with other tech companies and academic institutions to innovate and improve hydrogen generation and engine performance. Cummins also participates in global environmental initiatives to push for broader adoption of clean energy technologies.
References
Hydrogen-Fueled Internal Combustion Engines: Cummins has started testing hydrogen-fueled internal combustion engines, aiming to utilize these engines in various on- and off-highway applications. These engines are designed to operate with zero carbon emissions when fueled by green hydrogen, produced using Cummins-manufactured electrolyzers.
Electrolyzer Technologies and Green Hydrogen Production: Cummins is also expanding its capabilities in hydrogen production, specifically through electrolyzers. They have established a new PEM (Proton Exchange Membrane) electrolyzer plant in Spain aimed at boosting the production capacity for green hydrogen.
Strategic Investments and Partnerships: Cummins is investing in various strategic initiatives to strengthen its hydrogen technology offerings. This includes forming joint ventures for hydrogen storage and transportation solutions and enhancing the fueling infrastructure, which are critical components for the widespread adoption of hydrogen technology.